1. Objective:
It is to investigate some of the ways that bus shelters can be improved with the use of IoT, to provide useful information to the public. A small scale prototype focusing on smart advertising in bus shelters is modeled and evaluated. The proposed solution is believed to provide insight on one way that create value for businesses which often use bus shelters to advertise their products or services.
2. Brief description
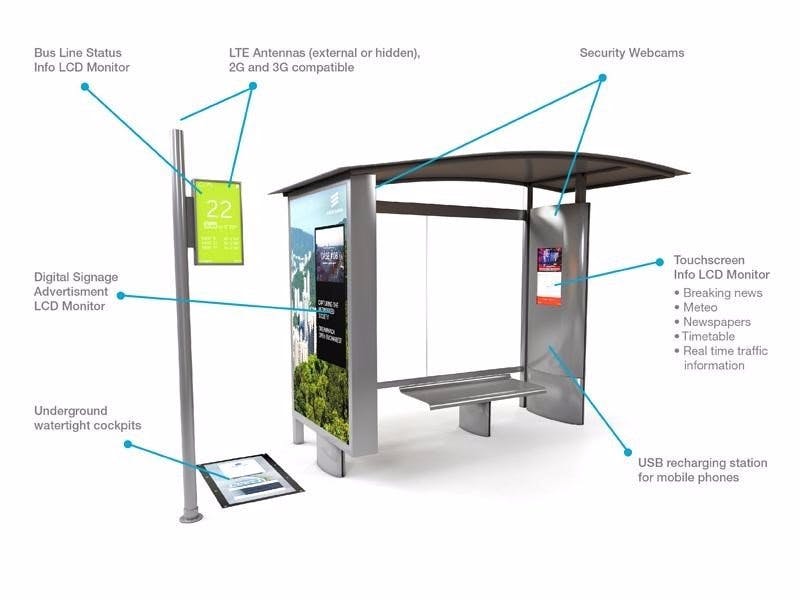
The focus of the project is about utilizing digital display of information in public spaces such as bus shelters. The information or content that we focus on in the research concerns digital advertisements or announcements from businesses, institutions and other points of interest around the city. This focus is expected to contribute to new smart advertising opportunities that create value for stakeholders. The integration of IoT in the smart bus shelter involves the use of sensors that collect contextual data from the commuters as well as the environment. Such data can be useful in the system’s decisions making, when it comes to what content is displayed on the screens. Another aspect that utilizes the sensors concerns automation of the bus shelter. This reduces unnecessary energy consumption by different appliances such as lights, display screens or heating in the bus shelter. Motion sensors can, for instance, influence the dimming of lights whenever the bus shelter is not in use for a set period of time.
3. Market Potential and Competitive Advantages
There can be two perspectives of looking at the added values.
User perspective: The user is the public transport commuter or a pedestrian who interacts with the smart bus shelter almost every day. Relevant information about the city can be of value to the user in terms of saving costs. From the user perspective, another key aspect that comes into play is the users’ experience in a bus shelter while he/she is waiting for the bus.
Stakeholder perspective: The stakeholders are the public transport providers, businesses and institutions that rely on smart bus shelters to convey their information to the commuters. Public transport providers consider services that convey traffic information such as a real time update of the bus position or the estimated time of arrival of the bus at the bus shelter. Businesses and institutions on the other hand invest in public announcements of events, or advertisement of local sales or offers. The focus of our research is on the business side and how the local businesses, institutions or outdoor media companies communicate information and connect to the commuters of different areas.
Bus Shelter
The smart bus shelter incorporates key functionalities and characteristics such as: Connectivity, interaction, digital maps, digital information display etc. In typical cases, connectivity is achieved using a 3G modem router that connects to the local mobile service provider. This allows the system to connect to the public transport web server as well as the cloud, whereby further information about the city is retrieved. Smart bus shelters deployed in Paris, include functionality that displays information and the happenings across the city, aimed to be a tour guide for tourists and other interested individuals.
4. Motivations
Motivations toward implementing smart bus shelters include improving how people use bus shelters to access information about the buses, and their surroundings.
Following are the uses of smart bus shelter system.
I. Public transport provider (Bus Company): Bus companies view smart bus shelters as an opportunity to provide better service to commuters in terms of information concerning arrival times for buses and their location on the map.
II. Businesses and institutions: Several businesses and institutions use bus shelters to advertise or communicate to the public. Most businesses attempt to advertise to their target market by strategically placing advertisement in the best (busiest) bus shelters, to widen the scope to more viewers.
III. Outdoor media companies: Bus shelters have an interesting business model in that they are primarily built and managed by private companies generally media companies, who agree to a long-term leasing agreement with cities or transportation agencies. An appropriate profile of the demographics and interests of bus shelter commuters can be useful to better monetize its digital signage advertising.
IV. Commuter: Refers to the person using the bus shelter. Smart bus shelters aim toprovide commuters with a better experience while waiting for the bus.




COMMENTS