500 MWe Prototype Fast Breeder Reactor (PFBR) is being commissioned at Kalpakkam, India. I&C systems of PFBR are classified as safety-critical (SC), safety-related (SR), and non-nuclear safety (NNS) systems [1,2]. Safety-critical systems play a prime role in achieving nuclear power plant safety.
Distributed Digital Control System (DDCS) is the design architecture adopted for Instrumentation & Control (I & C) of PFBR. DDCS is implemented using three-tier architecture wherein the bottom tier consists of control nodes, the middle tier comprises process computer (server), and the top tier consists of display stations as shown in Fig. 1.
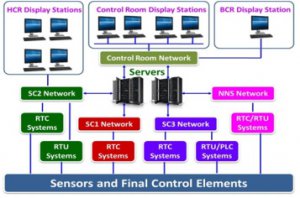
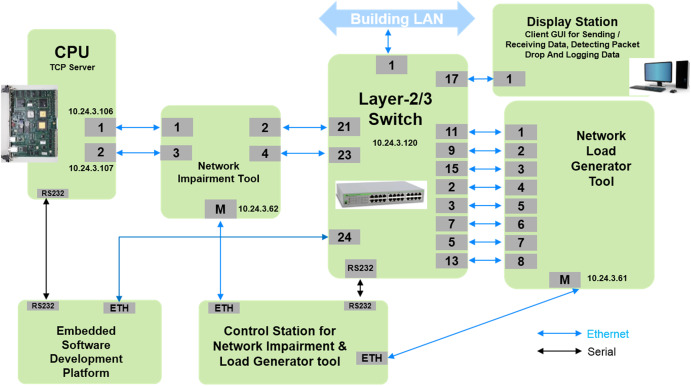
Field sensors & actuators are controlled by control systems placed in different locations connected to the centralized servers and display stations via switched local area networks. The TCP protocol is used for implementing Network layer functionalities of TCP/IP protocol, thereby assuring reliable connection-oriented data communication among various nodes. Regarding timing requirements for ethernet data, all safety-related nodes communicate data every second (scan interval).

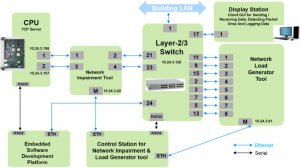
Ethernet communication for RTC systems is implemented by dual redundant TCP/IP offload modules (Network modules) available as pre-developed commercially available components from Wiznet(NM7010B+)

COMMENTS